20+ Animal And Plant Cell Diagram Labeled
Plant And Animal Cells Diagram Quiz Biological Science Picture Unlabeled Blank Animal Cell Diagram To Label Animal Cell To Label 7th Grade Cell Worksheets Globalexotica Net. A cell wall - normally composed of cellulose- on the outside of the cell.
Plant Cell Diagram Black And White.

Animal and plant cell diagram labeled. Unlabeled animal and plant cell diagram. Listed below are the Cell Organelles of an animal cell along with their functions. An improved method to screen Fc function of immunoglobulin products was developed using CMV kodecytes10 and FSL antigen constructs have been printed onto silica to create a convenient array for antibody identification4 Measles virions MV were fluorescently labeled to monitor binding to DC-SIGN expressing CHO cells using flow cytometry7 Carbohydrate FSL Constructs11 have been.
Square or rectangular in shape. Allows materials in and out. Present and lies in the centre of the cell.
A bacteria diagram clearly helps us to benefit extra about this unmarried cell organisms that have neither membrane-bounded nucleolus or organelles. 7 rows Animal cells usually have an irregular shape and plant cells usually have a regular shape. The typical characteristics that define the plant cell include cellulose hemicellulose and pectin plastids which play a major role in photosynthesis and storage of starch large vacuoles responsible for regulating the cell.
This is rigid so it gives the plant cell its shape. Have chloroplasts and use photosynthesis to produce food have cell wall made of cellulose A plant cell has plasmodesmata - microscopic channels which traverse the cell walls of the cells one very large vacuole in the center are rectangular in shape Animal Cells. While animal cells may have many tiny vacuoles a plant cell usually has a single large vacuole which serves as a storage tank for food water waste products and other materials.
The vacuole has an important structural function as well. Irregular or round in shape. There are various organelles present within the cell and are classified into three categories based on the presence or absence of membrane.
Also Read Different between Plant Cell and Animal Cell. Animal Cell Nucleus Plant Cell Cytoplasm Cell membrane Mitochondria Vacuole Chloroplast Cell Wall. Plant Cell Diagram Animal Cell Diagram Featured in this printable worksheet are the diagrams of the plant and animal cells with parts labeled vividly.
Learn the cell structures and how to identify and label themLike. What Is An Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring and Plant Cell Organelles Cake. The structure labeled e is called cpu of the cell where the genetic material resides.
Which of the following organelles does an animal cell NOT have. The Cell Organelles are membrane-bound present within the cells. Which of the following pair structures do not have similar functions.
Present and lies on one side of the cell. This may be useful as a printable poster. Blank Animal Cell Diagram To Label Human Body Anatomy Animal Cell Clipart Labeled.
It is made of several layers of parallel fibres and the gaps are filled in with jelly-like substances eg. Assembling cells from ready-made components in form of stickers. Nucleolus A round structure in the nucleus that makes ribosomes.
Present but are very rare. Well-Labelled Diagram of Animal Cell. PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLPLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS SSS Organelle Function Cell Membrane A double layer that supports and protects the cell.
Biology Multiple Choice Quizzes Plant Cell And Animal Cell Diagram Quiz Unlabeled animal cell diagram. The cell membrane is a double-layered membrane made up of phospholipids that surrounds the entire cell. Vacuole Stores food and water.
This enhanced visual instructional tool assists in grasping and retaining the names of the cell parts like mitochondrion vacuole. In addition to the chloroplast the mitochondrion and the nucleus are cut through revealing their internal structures.
83 Comparison Of Organelles In Plant And Animal Cells
Plant cells have chloroplasts because they make their own food. So even though plants and animals are very different organisms they have some very similar structures within their cells.
Solved 8 Compare And Contrast The Differences Between Pl Chegg Com
Differences Between Plant And Animal Cells The significant differences between plant and animal cells.

Comparison of organelles in plant and animal cells. Figure 48 these figures show the major organelles and other cell components of a a typical animal cell and b a typical eukaryotic plant cell. One organelle present in animal cells but absent in virtually all plant cells is the centriole. The lysosomes are the cells garbage disposal In plant cells the digestive processes take place in vacuoles.
Vacuoles are small Lysosomes are common Both Cell Membrane Nucleus Nuclear Membrane Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Mitochondrion Vacuole Lysosome Plant. Based on the table above it shows that both animal and plant cells have similar structure given the fact that they are eukaryotic cells. A plant cell usually has a single large and prominent vacuole which is a bladder-like structure containing water and other solutes thus serving as a storehouse of the cell.
Each difference will now be discussed in detail. Enzymes within the lysosomes aid the breakdown of proteins polysaccharides lipids nucleic acids and even worn-out organelles. The Difference Between Plant and Animal Cells While both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share many similarities they also differ in several ways.
Every eukaryotic cell animal cells plant cells you name it is enveloped by a plasma membrane. Plant and animal. They also have the same membranes cytoskeletal elements and cytosol.
Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth and Rough Present. Round irregular shape Rectangular fixed shape Chloroplast. Animal cells may or may not contain one or many smaller vacuoles.
29 rows Both plant and animal cells comprise membrane-bound organelles such as endoplasmic. A membrane-bound fluid-filled sac inside plant and animal cells. Food vacuoles of the Amoeba digest smaller cells captured by phagocytosis.
Plant and animal cells have organelles to help control organize and maintain the cell. They have membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus endoplasmic reticulum mitochondria lysosomes Golgi apparatus and peroxisomes. One example of this is that plant cells have chloroplasts that allow them to perform photosynthesis for energy but animal cells do not have chloroplasts since they get their energy elsewhere.
Animal cells dont have chloroplasts. Cell nucleus endoplasmic reticulum cell membrane cytoplasm and. Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuoles are large and few Lysosomes are uncommon.
It is very rare. Organelles are found in Eukaryotic cells and are tiny structures inside cells that carry out different functions to insure that homeostasis is maintained. 13 rows Comparison of Cell Organelles of Plant Cell and Animal Cell.
Contractile vacuoles of protists such as the Paramecium are specialized organelles for expelling excess water. Introduction to the Cell Guided Notes. Plant and animal cells have many of the same organelles.
In animals the centriole is present and. Differentiate between plant and animal cells Unicellular organisms consist of just one cell that carries out all life. Learn about the key differences.
The major differences between animal and plant cells include the presence of a cell wall chloroplasts and large vacuoles in plant cells but not in animal cells. Plant cells have large central vacuoles that occupy much of the cell volume. Comparing Plant Animal and Bacteria Cells You should know You should be able to All living organisms are made of cells Draw cells that are seen under a light microscope Cell organelles carry out functions within eukaryotic cells.
Animal cells have another set of organelles not found in plant cells. These are functions that are mainly done by the.
28+ Animal Cell Nuclear Membrane Function
Transcription copying of deoxyribonucleic acid DNA in the nucleus and translation decoding of the message into protein in the cytoplasm. Holes in the nuclear membrane that allow RNA to move in and out of the nucleus.
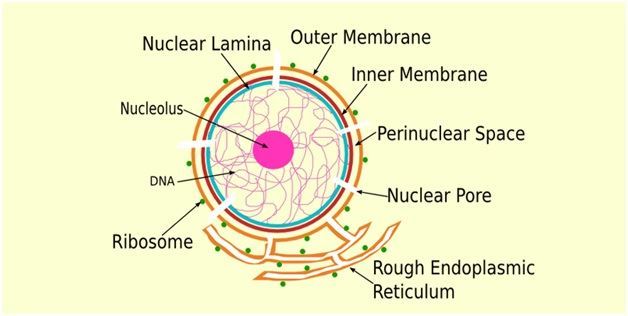
Nuclear Membrane Structure Function Of Nuclear Membrane
It is found in both plant and animal cell.

Animal cell nuclear membrane function. Start studying Names and Functions of the Organelles in Plant and animal cells. Nucleus The control center of the cell. The functions of nuclear membranes can be more easily grasped by knowing its structural components.
A cell has many jobs such as building proteins converting molecules into energy and removing waste products. Animal Cell Definition Structure Parts Functions And Diagram Dna contains all the. A nuclear membrane is a double membrane that encloses the cell nucleus.
The nuclear membrane includes an array of small holes or pores that permit the passage of certain materials such as nucleic acids and proteins between the nucleus. Ribosome small organelles composed of rna rich cytoplasmic granules that are sites of protein synthesis. The nuclear membrane has the function of protecting the dna inside the nucleus from surrounding exterior substances.
Here one must be aware of a fact that prokaryotic cells dont have membranes around their nuclei. In eukaryotic cells the double membrane enclosing DNA and any other genetic material is known as nuclear membrane. The animal cells consists of centriole which carries out cell division.
Cytoplasm Jelly-like fluid that surrounds and protects the organelles. Compared to the structure of the bacterial cell this gives greater control. As stated before animal cells are eukaryotic cells with a membrane-bound nucleus.
Animal cell diagram and functions. Cell Membrane A double layer that supports and protects the cell. Animal cell nucleus has a lot of functions like controlling all the cellular activities and carrying the hereditary information of the cell.
It serves to separate the chromosomes from the rest of the cell. Additionally the nuclear envelope can regulate what. The animal cells have an organized nucleus with a nuclear envelope.
In 1831 Robert Brown first discovered the nucleus. Lysosome Contains digestive enzymes that destroy damaged organelles and invaders. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Contains the DNA Nuclear Membrane Surrounds the nucleus. It separates the fluid inside the nucleus of a cell from. Furthermore these cells exhibit the presence of DNA inside the nucleus.
They also comprise other membrane-bound organelles and cellular structures which carry out specific functions necessary for a cell to function properly. This genetic information is called deoxyribonucleic acid dna. The presence of a nuclear membrane in eukaryotes permits separation of the two phases of protein synthesis.
The nuclear membrane also regulates which substances can enter or exit the nucleus. The function of the nuclear membrane in an animal cell is to hold the DNA inside the nucleus in order to protect it from surrounding substances. Animal cell diagram nuclear membrane.
It separates the fluid inside the nucleus of a cell from the material outside. The nucleus is a dense and most significant component of the cell. The eukaryotic cells have cell organelles that are lacking in prokaryotic cells except the ribosomes.
Allows materials in and out. Cytoplasm is supposed to be the matrix or gel like substancefluid present inside the cell. Along with that it possesses locomotory structures.
Function of Nuclear Membrane The nuclear membrane keeps your DNA inside the nucleus to protect it from surrounding substances in the cytoplasm. Separated from the cytosol a compartment called the nucleus store genetic material in eukaryotic cells. The animal cell functions nuclear envelope or nuclear membrane is membranes that separate nuclei of eukaryotic cells and the cytosol.
The nuclear membrane also known as the nuclear envelope surrounds every nucleus found in animal cells.
84 Vacuole Structure In Animal Cell
Vacuole in biology a space within a cell that is empty of cytoplasm lined with a membrane and filled with fluid. Vacuoles - Storage Bins to the Cells Vacuoles are storage bubbles found in cells.

Vacuole Definition Structure And Functions Biology Dictionary
Its one of the largest organelles found in cells and its shaped like a large sac.
Vacuole structure in animal cell. Alternatively they may be prepared artificially in which case they are called liposomes. Especially in protozoa single-celled eukaryotic organisms vacuoles are essential cytoplasmic organs organelles performing functions such as storage ingestion digestion excretion and. It is a space or vesicle within the cytoplasm of a cell enclosed by a membrane and naturally containing fluid.
The function and significance of vacuoles differs greatly according to the cell type. The membranes are composed of phospholipids. Thus this membrane does not allow harmful substances present in here from entering and harming the rest of the cell.
Know what is cell structure in Biology Definition Process Types Meaning Examples along with important questions. Sometimes a single vacuole can take up most of the interior space of the plant cell. The vacuole structure is designed to aid this important cell organelle which is one of the key plant and animal cell differences.
A vacuole is a membrane-bound cell organelle. The nucleus in plant cells is lens-shaped and peripheral in position due to a large central vacuole. Structure Of Animal And Plant Cell Download Scientific Diagram Both all animals and plants are made of cells.
A vesicle is a small structure within a cell consisting of fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer. The most important structures of plant and animal cells are shown in the diagrams below which provide a clear illustration of how much these cells have in common. The main function of vacuoles in animal cells is to isolate and remove waste products from the other organelles and the cytoplasm.
Vacuoles generally have acidic pH values. Central Vacuole The central vacuole is found only in plant cells. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion exocytosis uptake phagocytosis and transport of materials within the cytoplasm.
Vacuoles means empty space are cavities in the cytoplasm especially in plant cells surrounded by a cytoplasmic membrane the tonoplast and filled with a watery fluid called the cell sap containing water and various substances in solution or suspended state. Animal Cells In animal cells vacuoles serve more subordinate roles such as assisting in endo- and exocytosis or basic storage of food and waste. However they are not prominent as in case of a plant cell.
It is filled with water and is pressurised like a balloon. A vacuole is an organelle in cells which functions to hold various solutions or materials. In animal cells vacuoles are generally small and help sequester waste products.
Vacuole Function in Animal Cells. The animal cell also contain a few small vacuoles. Although animal cells contain vacuoles they do not contain large central vacuoles.
Its membrane the tonoplast helps to separate its contents from those floating in the cytoplasm. It is spherical in animal cells. This includes solutions that have been created and are being stored or excreted and those that have been phagocytized or engulfed by the cell.
A cell is the basic unit of life. They are surrounded by a thin membrane and filled with fluid and any molecules they take in. In animal cells the vacuoles can be anywhere in the cells cytoplasm except in the nucleus or cell membrane.
They are found in both animal and plant cells but are much larger in plant cellsVacuoles might store food or any variety of nutrients a cell might need to survive. The membrane surrounding the vacuole is known as tonoplast. Structure of Cell.
A vacuole is a structure found in animal plant bacteria protist and fungi cells. In plant cells vacuoles help maintain water balance. Vacuoles may accumulate food or any diversity of nutrients a cell may require to survive.
In fact vacuoles move around in the cell in order to dispose of any waste they hold. The components of the vacuole known as the cell sap differ from that of the surrounding cytoplasm. They are found in both animal and plant cells but are much bigger in plant cells.
Because of which it is the most prominent cell organelle in most of the plant cells. A vacuole is a membrane bound structure found in the cytoplasmic matrix of a cell. Vacuoles have a simple structure.
The open spaces found in the cytoplasm are the vacuole. In animal cells vacuoles tend to play a lesser role.
60 Animal Cell Under Transmission Electron Microscope
The image is magnified and focused onto an imaging device such as a fluorescent screen or a. Some variation of this microscope can also penetrate down to the subatomic particles like electrons.
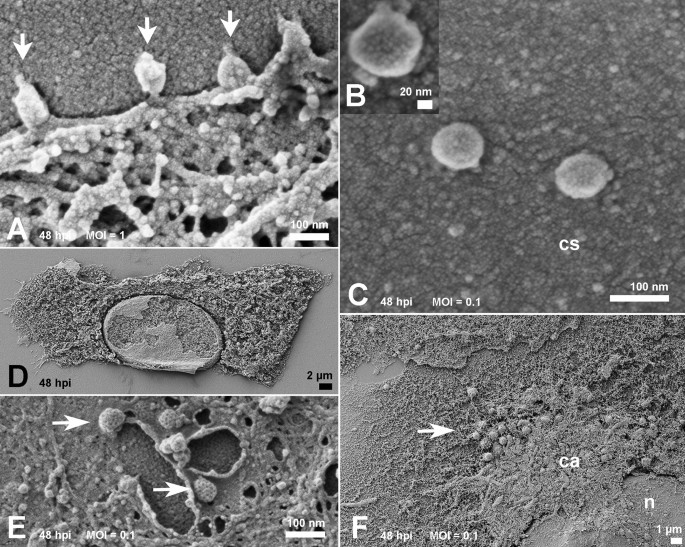
Ultrastructural Analysis Of Sars Cov 2 Interactions With The Host Cell Via High Resolution Scanning Electron Microscopy Scientific Reports
Spirogyra Under Microscope 10x.
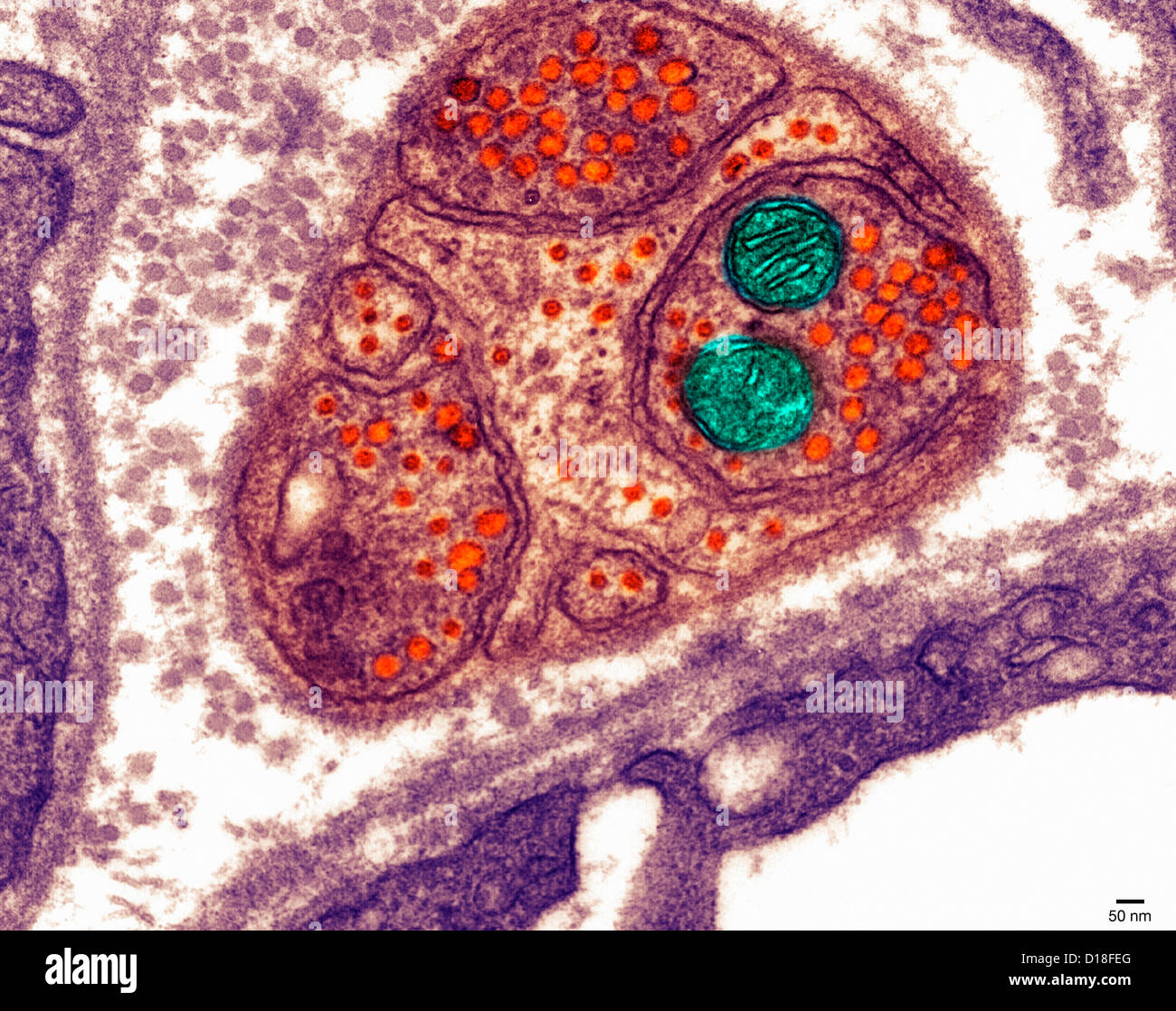
Animal cell under transmission electron microscope. Methods In Cell Biology. Methods In Cell Biology. Blood opens an overview page on the different blood cells.
The cell wall nucleus vacuoles mitochondria endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus and ribosomes are easily visible in this transmission electron micrograph. You see that many features are in common. Magnification 50 000x Transmission Electron Micrograph Tem.
Monster Designs Animal Cell Under An Electron Microscope. Microscope Cell Images Animal Cells All Living Things Are Made Up. Under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use distribution and reproduction in any medium provided the.
Charles Daghlian Dartmouth Electron Microscope Facility via Wikimedia Commons. However no obvious structural damage was apparent and several repeated scans gave the same images. Commencing circa 1950 the development of the transmission electron microscope revolutionized microscopy progressively bringing it.
This would allow the cell to be viewed in a lot more detail than what it was with a light microscope however the image is only ever produced in shades grey. Fast Transmission Electron Microscope TEM. The microscope can not only distinguish between individual atoms but even see them when they were about only 04 angstroms apart half the length of a chemical bond.
Exercise 3 Cells Organelles And Inclusions. Liquid cell electron microscopy e. The plant cell as more rigid and stiff walls.
The diagram below shows the general structure of an animal cell as seen under an electron microscope. The nature of the image depends on the type of light or electron microscope used and on the way in which the cell or tissue has been prepared for observation. Thats the major difference between plant and animal cells under microscope.
Human and animal mitochondria. You know Animal cell structure contains only 11 parts out of the 13 parts you saw in the plant cell diagram because Chloroplast and Cell Wall are available only in a plant cell. Usb Microscope Software Windows 10.
Isolated mitochondria as well as cell suspensions to be completed in. However the transmission electron microscope uses a high voltage beam which passes through a thin sample showing the internal structure of the cell. These are both specific types of.
Table D leads to images of electron microscopes or protocols for tissue preparation. Electron microscope The images from the transmission electron microscope show a razor-thin layer just two atoms thick of two atoms bonded together. The development of electron microscopes has greatly extended the ability to resolve sub-cellular particles and it has provided new information on the organization of plant and animal tissues.
Trachea epithelium showing ciliated cells cells with hair-like projections. The Great Story Iii An Animal Cell A Eukaryote Before The. Transmission Electron Microscope Tem Micrograph Showing Several.
Below the basic structure is shown in the same animal cell on the left viewed with the light microscope and on the right with the transmission electron. Transmission Electron Microscope TEM Zoology for IAS IFoS and other competitive exams. Here is an electron micrograph of an animal cell with the labels superimposed.
In this lab you observe typical undifferentiated plant cells parenchymaYou should have note the characteristics that plant cells share with all other eukaryotic cells the nucleus and membrane-bound organelles and also note the characters where plant cells differ from animal cells large central vacuole plastids and cell wall. Animal cells have a basic structure. All you need for this is a microscope with a basic transmitted light source and enough magnification to resolve individual yeast cells.
Transmission and some scanning electron microscopic images oforgans. Head and mouth of a. In transmission electron microscope TEM a beam of electrons is transmitted through the section of a specimen and an image is formed by the interaction of the electrons transmitted through the specimen.
The animal cell is more fluid or elastic or malleable in structure. What can be seen under a electron microscope. Under the intense radiation of the electron microscope 011 electron per Å 2 the question of viability of cells naturally arises because the amount of radiation absorbed during highmagnification imaging is sufficient to cause cell death.
The transmission electron microscope.


